Bladder Exstrophy-Epispadias-Cloacal Exstrophy Complex – Cause, symptoms, Epidemiology, Diagnosis and treatment
Bladder exstrophy-epispadias-cloacal exstrophy complex is the most severe form of the BEEC (Bladder exstrophy-epispadias complex), constituting 10% of all the cases. In this condition, an abdominal wall defect causes bladder and large intestine extrusion, leading to anal, genital, and colon abnormalities. BEEC is a rare, congenital, multisystemic condition and involves anomalies in the musculoskeletal, urinary, and genital systems. The majority of treatment of BEEC is surgical, and it is usually done in phases. Several long-term consequences of this difficult pediatric urological condition necessitate a comprehensive approach to therapy.
BEEC
BEEC is a term that describes a range of anterior midline
defects, from glandular epispadias to multisystem defects like cloacal
exstrophy. The word exstrophy comes from the Greek word
"ekstriphein," which means "turn inside out." Within the
BEEC spectrum, there are three unique conditions. These are - classic bladder
exstrophy, epispadias, and cloacal exstrophy.
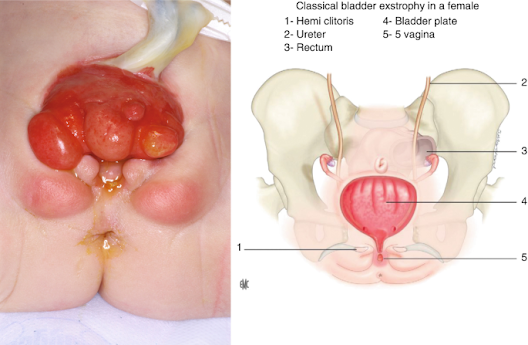
Classic bladder exstrophy is the most common presentation
form of BEEC, constituting 60% of all cases. It is defined by an open,
inside-out bladder and an exposed dorsal urethra on the lower abdomen wall's
surface. The umbilicus is positioned lower, and pubic bones on both sides of
the bladder template can be felt. External genitalia involvement is present in
all patients, and most have a palpable inguinal hernia.
BEEC's mildest manifestation is epispadias. It is
characterized by non-closure of the urethral plate and an atypical dorsal
urethral position, accounting for 30% of all BEEC cases. Males have an ectopic
meatus or a mucosal strip on the penile dorsum, whereas females have a urethral
cleft.
Cause and symptoms of Bladder exstrophy-epispadias complex
The specific process that causes bladder exstrophy in the
embryo is unknown. The urogenital membrane is thought to break down prematurely
because the lower abdominal wall fails to develop. The outcomes include an open
bladder plate, a low-placed umbilicus, and a diastasis of the pubic bones.
Above the genital tubercle, the cloacal membrane ruptures, resulting in a penis
with an open dorsal surface that is continuous with the bladder plate. The type
of defect is determined by when the rupture occurs, resulting in the different
forms of BEEC.
A mix of genetic and environmental factors has also been
discovered to play a role in the disease's etiology. Male sex, race, parental
age, and pre-conceptional mother exposure to smoking, certain drugs, and
alcohol have all been linked to an elevated incidence of BEEC in studies.
Cloacal exstrophy typically affects the pelvis. Eversion of the innominate bones and widening of the pubic symphysis are frequent symptoms. The pelvic abnormalities in cloacal exstrophy are more severe and asymmetric, and they can result in hip dislocation, necessitating an ultrasonographic examination of the hip joints. In bladder exstrophy and as part of the OEIS syndrome (omphalocele, cloacal exstrophy, imperforated anus, and spinal defects), spinal anomalies such as neural tube malformations can arise.
Several other skeletal and limb malformations are frequent
in affected children, especially with cloacal exstrophy, and should be
considered during initial monitoring and long-term management planning.
Cloacal exstrophy is almost often linked to gastrointestinal
abnormalities. Omphaloceles can be identified in cloacal exstrophy in 88-100 %
of patients. In up to 46% of instances, gastrointestinal malrotation and short
bowel are present, resulting in absorptive problems in 25% of children.
Patients with cloacal exstrophy may also have various urologic problems such as
ureteropelvic junction blockage, horseshoe kidney, ureteral ectopy, megaureter,
and ureterocele in addition to the bladder defect.
Epidemiology of Bladder exstrophy-epispadias complex
The incidence of BEEC has been recorded in a variety of
ways, including subtypes, ethnicity, and sex ratio. Cloacal exstrophy is the
rarest form of the spectrum, with a prevalence of 0.5 to 1 per 200,000 live
births. The prevalence of cloacal exstrophy-related pregnancies could be as
high as 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 50,000 due to greater rates of stillbirth and
pregnancy termination.
Diagnosis and treatment of Bladder exstrophy-epispadias complex
Clinical observation after delivery is used to diagnose
bladder exstrophy in children. Bladder exstrophy, on the other hand, may
usually be detected between the 15th and 32nd weeks of pregnancy with
high-resolution real-time ultrasonography, even during regular obstetric
treatment. The absence of a fluid-filled bladder, a low-set umbilicus, tiny
genitalia, pubic rami expanding, and rising lower abdominal mass as the
pregnancy progress have all been found to be reliable criteria for prenatal
diagnosis of bladder exstrophy.
Only ambiguous instances are subjected to fetal magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) and color Doppler ultrasonography. Although prenatal
intervention is not required, early detection allows for delivery in a
pediatric center equipped to handle this difficult deformity and thorough
family counseling.
In bladder exstrophy, treatment aims to close the bladder
and abdominal defect while maintaining renal and sexual function. A pelvic
osteotomy is always recommended in cases of failed exstrophy repair or cloacal
exstrophy. Cloacal exstrophy is more difficult to treat surgically, and it
usually necessitates neurosurgery, gastrointestinal, and urological treatments.
Repair of spinal dysraphism and myelocystocele, if present,
is included. It also includes repair of the omphalocele, external genitalia,
and anorectal malformations, along with the closure of the bladder, urethra,
and bony pelvis. However, urinary continence in these children is usually
achieved with bladder augmentation and intermittent catheterization.
References
Baradaran, N., & Gearhart, J. P. (2010). Bladder
exstrophy-epispadias-cloacal exstrophy complex: a contemporary overview. Neoreviews,
11(12), e705-e713. https://doi.org/10.1542/neo.11-12-e705
Exstrophy-epispadias complex. [Online] NIH-GARD. Available
at:
https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/2207/exstrophy-epispadias-complex







No comments